Structural Damping Isolation System
As we all know, earthquakes are the most terrifying natural disasters, causing more casualties than all other natural disasters combined. The traditional concept of building earthquake resistance is head-to-head. When an earthquake comes, first ensure that the building does not collapse, mainly to achieve structural safety, and then to achieve other protections by the way - for example: personnel can pass the first time after receiving an earthquake warning (crouch- After the main shock is over, take emergency items and evacuate to the outdoor emergency shelter temporarily according to the earthquake emergency procedures you have learned, until the aftershocks of this earthquake are over. Then go back home to clean up the "endgame".
The concept of seismic isolation technology is to overcome rigidity with flexibility, and to achieve "multi-protection" of structures, non-structural components and facilities and equipment during earthquakes, forming a "safety island" for the city, and realizing the normal use of buildings during earthquakes. Uninterrupted.
Still not enough? For more, see below:
The traditional seismic technology is to firmly connect the upper building structure and the foundation, so that the energy of the ground movement during the earthquake is transmitted to the upper structure through the foundation, causing the structure to vibrate and deform. When the structure exceeds its structural strength, it occurs. damage or even collapse. In order to resist the damage of earthquake, the traditional seismic technology of buildings is realized by increasing the size of beam-column section, increasing beam-column reinforcement and improving the strength of building materials. However, this method of strengthening the rigidity will lead to the result that the greater the rigidity of the structure, the stronger the seismic action transmitted to the upper structure. To put it simply, the anti-seismic thought of traditional buildings can be summarized as "to make rigidity with rigidity".
Building shock absorption technology (structural energy dissipation shock absorption technology) is to set energy dissipation devices (dampers) in some parts of the structure (such as supports, shear walls, joints or connectors), through which friction, bending ( or shear, torsion), elastic-plastic (or viscoelastic) hysteretic deformation to dissipate or absorb the energy input to the structure by the earthquake (convert vibration or vibration energy into other forms of energy dissipation, such as heat), in order to reduce the main body The seismic response of the structure can avoid the damage or collapse of the structure and achieve the purpose of shock absorption control.
Building seismic isolation technology is to set seismic isolation devices (composed of shock isolators, damping devices, etc.) between the foundation or the substructure and the superstructure of the building to form a seismic isolation layer, isolate the seismic energy from transmitting to the upper structure, and reduce the input to the upper structure. The seismic energy of the superstructure (can reduce the seismic energy by about 80%), while extending the natural vibration period of the superstructure, reducing the seismic response of the superstructure, meeting the expected seismic and seismic requirements, and ensuring the safety of the building more reliably.
Tool overview
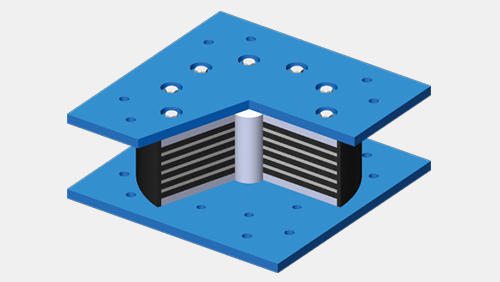
The natural rubber bearing is a shock isolation bearing composed of connecting steel plates, rubber layers and stiffening steel plates. The support has high vertical bearing capacity and good horizontal deformation capacity. At present, it has been widely used in the seismic design of buildings, bridges and other structures, and has achieved good economic and social benefits.
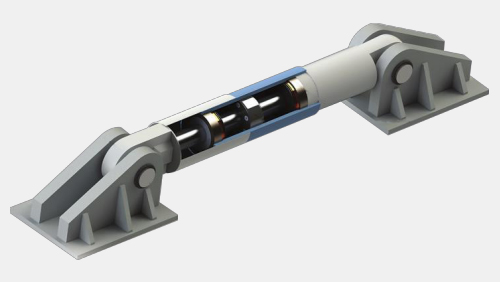
Architectural viscous damper is an oil-cylinder structure filled with damping medium. The reciprocating motion of the piston drives the flow of the internal medium to produce a damping effect, and then convert kinetic energy into thermal energy. Building viscous dampers are mainly suitable for schools, hospitals, stadiums and high-rise buildings in earthquake-prone and typhoon-prone areas.
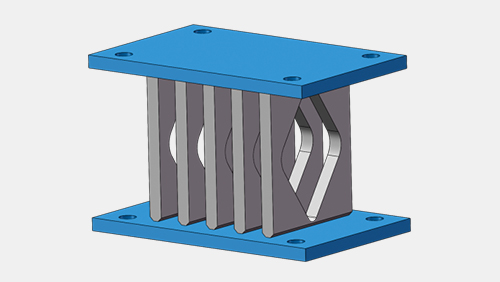
Metal buckling dampers are usually made of low-yield stress steel, which is a kind of energy-dissipating damping device in passive control of structures. During earthquake or wind vibration, the plastic yield hysteretic deformation of mild steel is dissipated into the structure. energy, so as to achieve the purpose of shock absorption. Mild steel has good low cycle fatigue properties and hysteresis properties. Metal yield dampers have the advantages of being sturdy and durable, maintenance-free for long-term use, and their seismic performance is not affected by temperature.